The fuses and circuit breakers are devices used in electrical circuits to interrupt the flow of electricity in case of overload. Both devices can be understood as safety systems to prevent an electrical overload from causing damage, both to the devices and to the electrical network.
The difference between fuses and switches lies in the way they work :
 |
 |
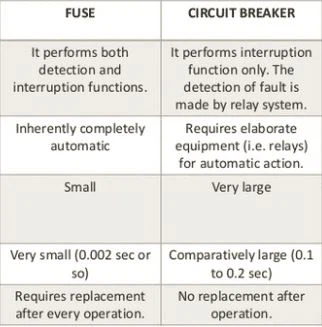
· Fuse: Consists of a metal piece or filament that breaks when heated above a certain temperature. When it breaks, the electric flow is interrupted. Fuses respond faster than switches, but affected fuses have to be replaced with new fuses
· Automatic switch: it has a switching mechanism that is activated when the electrical voltage (voltage) increases.
Fuse Operation
The fuses are made of a metal filament enclosed in a glass or ceramic casing.
Fuses allow electricity to pass through the filament connecting the different circuits in the installation. If an overload occurs. The filament will heat up and melt, breaking and preventing the flow of electricity to continue.
In general, fuses elements are very sensitive and above the level for which they were designed, they take very little time to break. Once a fuse has broken you have to replace it with a new one.
Most of fuses are made to withstand different voltages. It is best to use fuses with a capacity slightly higher than the current that will normally pass through it. In this way, we can adequately protect the devices and equipment connected to the network.
Circuit Breaker Operation
The circuit breakers, also called automatic, breaker, tablet or circuit breaker, also shut off power when overloaded but do so using a switch.
The switch used can use an electromagnet or a bimetallic strip. In both cases the operating principle is similar.
When the switch is in the on position, electrical current can pass from one terminal to another through the electromagnet or the bimetallic strip.
When the electric current exceeds a certain voltage level, the magnetic force on the electromagnet increases until it is able to push the metal lever of the internal switch and interrupt the electrical flow.
In the case of bimetallic strips, they are bent until the switch lever is pushed.
Unlike fuses, when automatic jumps it is not necessary to replace it with a new one. Simply return the switch to the on position.
Circuit breakers are usually found in a box where there are switches for different parts of the electrical circuit. For example, in a house, there may be a switch for the lighting circuit and another for the plugs or for different areas of the house.
Another common use of circuit breakers is ground fault detection circuit breakers. These switches respond to the balance of the electric current and not to overload.
If there is no balance in the electric current, the switch cuts its path, avoiding discharges. They are very useful in bathrooms and kitchens where there is an increased risk of electric shock from the continuous use of electrical appliances near water.
Related News
- Advantages And Disadvantages Of Fuses And Switches
- The First Sunken Well Garage In China
- GRL RT18series Fuse Holder
- What Are Disconnect Switches?
- The First China International Consumer Products Expo
- A Billiards Game At GRL!!!
- World Smile Day 2021
- Tariffs Adjustment On Certain Steel Products
- Celebrate The International Labour Day
- GRL Isolator Switch







