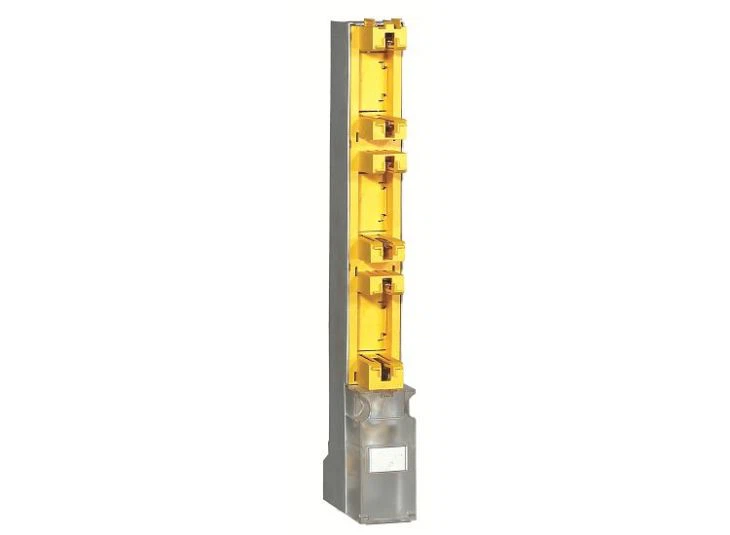
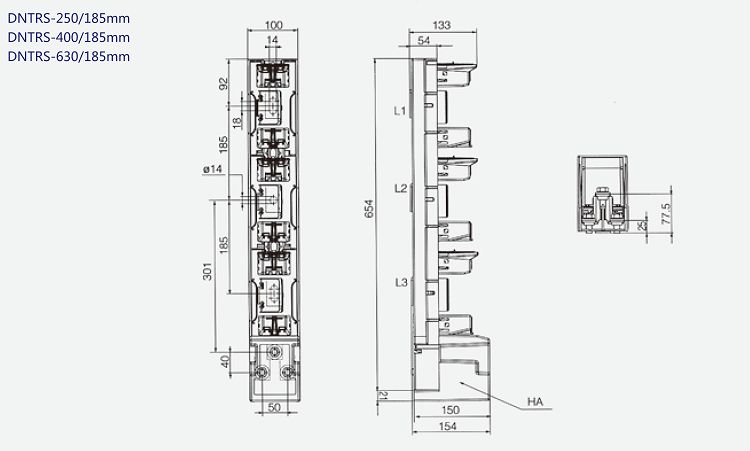
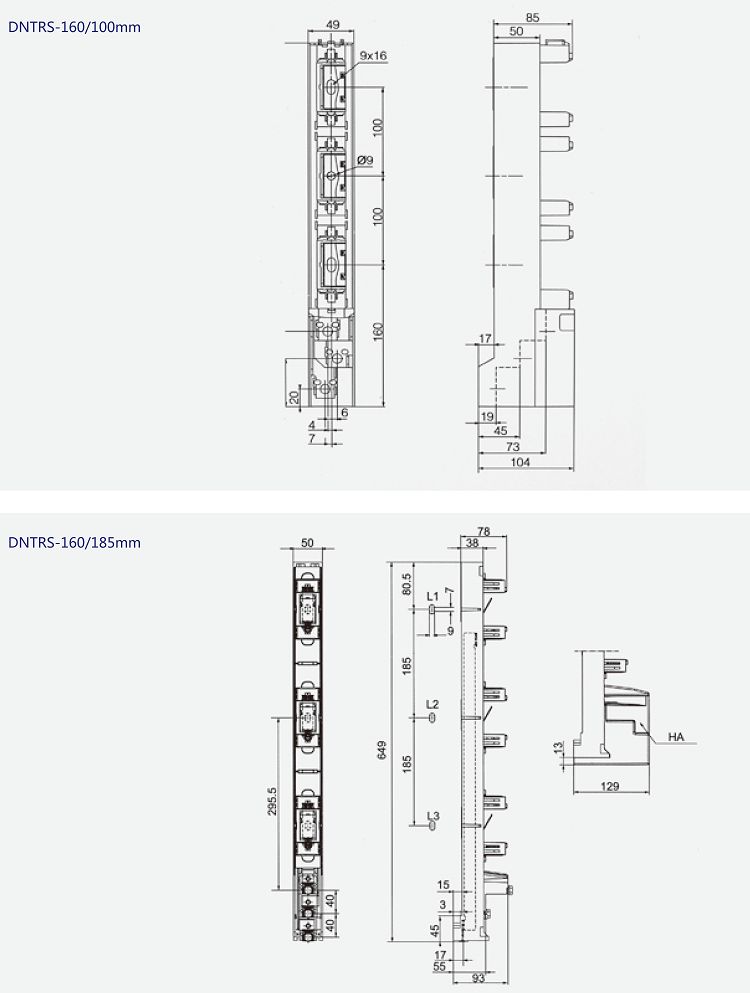
Strip Fuse Base
The strip fuse base is suitable for AC 50Hz, rated insulated voltage to 690V, convention heating current up to 630A. It is intended for fuse links with blade contacts. The base is made of fibreglass reinforced moulding material with high mechanical strength and high thermal resistance. It is an electrical component that is installed in the circuit to ensure safe operation of the circuit.
- Product Details
- Parameter
- Product Acessories
- Download
-
NT Base This product conforms to IEC-60296 and the GB13539 standards.The product has been used as a mounting/dismantling and replacing tool for NT/NH/RT0 Body. Its rated volatge is rated AC 1000V, and rated current up to 1250A(AC 50Hz)
Conventional Current (A) 160 (100) 250 400 630 Rated Voltage (Ue) 660VAC 380VAC Rated Insulation Voltage (Ui) 800VAC Rated Current (Ie) AC 380V AC-21B 100, 160A 250A 400A 630A AC 660V AC-21B 100, 160A 250A 400A 630A Fuse Type NH00 NH1 NH2 NH3 In electronics and electrical engineering, a fuse is an electrical safety device that operates to provide overcurrent protection of an electrical circuit. Its essential component is a metal wire or strip that melts when too much current flows through it, thereby interrupting the current. It is a sacrificial device; once a fuse has operated it is an open circuit, and it must be replaced or rewired, depending on type.
Fuses have been used as essential safety devices from the early days of electrical engineering. Today there are thousands of different fuse designs which have specific current and voltage ratings, breaking capacity and response times, depending on the application. The time and current operating characteristics of fuses are chosen to provide adequate protection without needless interruption. Wiring regulations usually define a maximum fuse current rating for particular circuits. Short circuits, overloading, mismatched loads, or device failure are the prime reasons for fuse operation.
A fuse consists of a metal strip or wire fuse element, of small cross-section compared to the circuit conductors, mounted between a pair of electrical terminals, and (usually) enclosed by a non-combustible housing. The fuse is arranged in series to carry all the current passing through the protected circuit. The resistance of the element generates heat due to the current flow. The size and construction of the element is (empirically)